
What’s the difference between radiation and contamination? When an instrument sends a scram signal, the control blades (which are held up by electromagnets) drop down by gravity, shutting down the reactor in less than one second. There are many instruments that are designed to automatically shut down the reactor if a parameter is outside its nominal range (for example, if the water temperature becomes too high). What is a ‘scram’?Ī scram is an automatic reactor shutdown. In other words, when the reactor is critical, it is operating at steady-state. ’Critical‘ is the term used to describe a reactor state in which the number of neutrons being produced equals the number being absorbed, which in turn produces the same number of neutrons. Reactor Engineering What does it mean to go ‘critical’? The rate at which an isotope undergoes radioactive decay is described by the isotope’s half-life, which is the amount of time it takes for half of any amount of that radioactive isotope to decay. Sometimes an atom will decay into an atom that is also radioactive producing a radioactive decay chain. When an atom decays it may become a different element, or the same element with a different number of neutrons (a different isotope of the same element).

Most elements have both radioactive and stable (non-radioactive) isotopes. Radioactive decay is the process through which some atoms revert to a more stable nuclear configuration by emitting energy (e.g., gamma rays, electrons, alpha particles). The neutrons produced in the reactor core get absorbed by fuel or core materials in fractions of a second.

Isolated neutrons have a half-life of 10.4 minutes and decay to stable hydrogen (H-1) – the neutron essentially splits into a proton and an electron.

How can you have neutrons without protons and electrons? Neutrons are invisible just like all forms of electromagnetic and particle radiation (except for the visible portion of the light spectrum). The name ‘heavy water’ is used because deuterium is twice as heavy as regular hydrogen. Deuterium is sometimes given the symbol ‘D’ so heavy water can be referred to as D 2O. Unlike a lot of isotopes, H-2 has a special name we can call it besides hydrogen: Deuterium. Heavy water is mostly just like ordinary water (H 2O) but with the regular hydrogen atoms (H-1) replaced by atoms with an extra neutron (H-2). However, different isotopes of the same element can have very different nuclear properties. Because different isotopes of the same element have the same number of protons and electrons, they behave similarly in their chemistry (they may behave slightly differently physically due to their different masses). A small amount of hydrogen (about 0.01%) has one proton one neutron, so it is referred to as H-2. For example, the most common isotope of natural hydrogen has just one proton a no neutron, so it is referred to as H-1. They are named using the letter abbreviation of the element and the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes are different versions of elements. While the reactor is running, the vast majority of neutrons are produced by the fission of U-235 in our fuel. This chain reaction can continue if there are enough fissile nuclei in a small enough space, and the neutrons don’t get absorbed by other materials or leak out from that space. This process is the fission chain reaction.
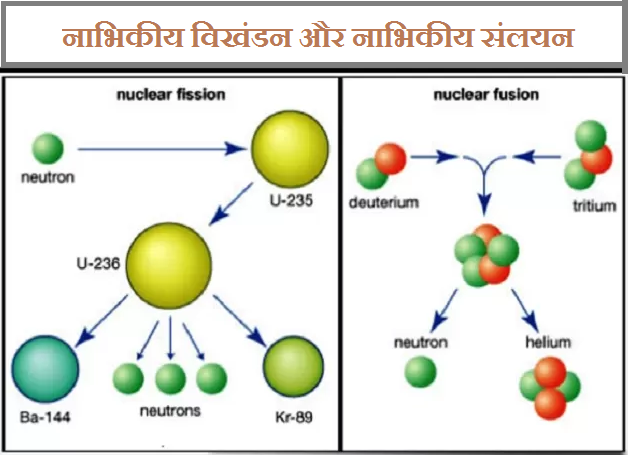
Those can hit other nearby uranium-235 atoms and cause those to fission, emitting more neutrons. What is a chain reaction?įor example, when a nucleus such as uranium-235 fissions, it emits neutrons. Some isotopes such as californium-252 can spontaneously fission, though most isotopes that are can undergo fission need some stimulation or disruption, such as the absorption of a neutron, in order to cause fission. At the MIT Reactor Lab uranium-235 fissions in the core to produce heat (which we don’t use) and neutrons (which we use for research and experiments). Fission is the nuclear process that involves the splitting of a nucleus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
